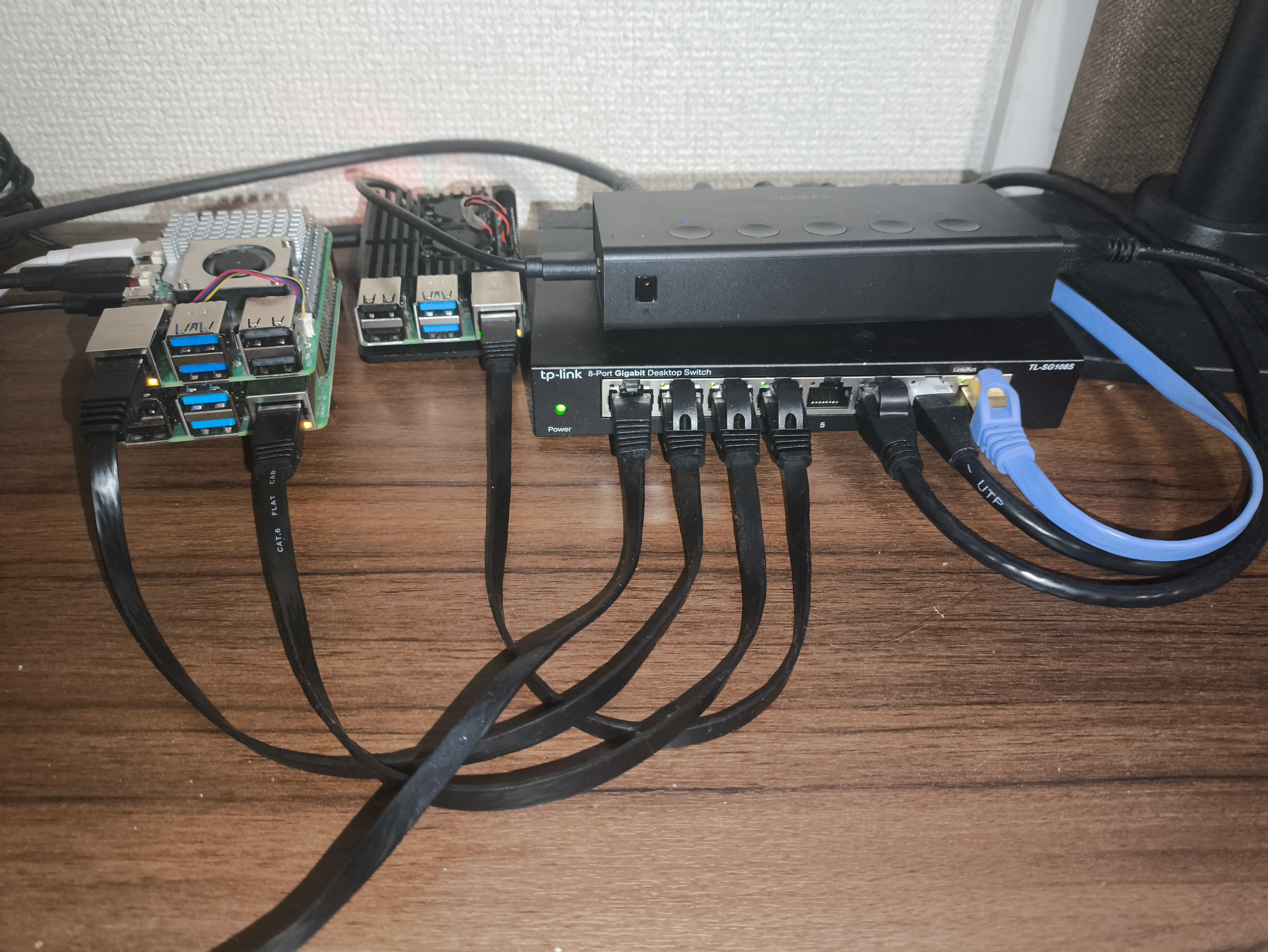
3台のRaspberry PiでおうちKubernetesを構築した
Date: 2024-12-28
## なぜ
## 使ったもの
### ハードウェア
- - Raspberry Pi 5 (Sapphire)
- - RAM 8GB
- - microSD 128GB
- - Control Plane
- -
- - Raspberry Pi 4B (Emerald)
- - RAM 8GB
- - microSD 128GB
- - Worker Node 1
- -
- - Raspberry Pi 4B (Ruby)
- - RAM 4GB
- - microSD 32GB
- - Worker Node 2
- -
### ソフトウェア
- - Ubuntu Server 24.04.1
- - Kubernetes: v1.32
- - CRI-O: v1.32
- - calico: v3.29.1
## Raspberry Piのセットアップ
今回はWindowsでRaspberry Pi Imagerを使った。ホスト名、
authorized_keysなど設定してからmicroSDにimageを焼けるので便利。bootしたら、ssh, ipアドレスを設定する。これ以降特に何も言及がなければ3台に同じ操作をしている。```bash
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sudo vim /etc/netplan/99-config.yaml
sudo netplan apply```
```/etc/ssh/sshd_config
PermitRootLogin no
PasswordAuthentication no```
```yaml:/etc/netplan/99-config.yaml
network:
version: 2
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: false
addresses:
- 192.168.1.110/24 # Raspberry PiのIPアドレス
routes:
- to: default
via: 192.168.1.1 # ルーターのIPアドレス```
## CRI-O, Kubernetesの導入
コンテナランタイムについて
まず、CRI-Oのドキュメントに従って、コンテナランタイムであるCRI-OとそのオーケストレータのKubernetesの最新のバージョンを確認してaptパッケージを追加する。
https://github.com/cri-o/packaging/blob/main/README.md/#distributions-using-rpm-packages
```bash
$ echo "KUBERNETES_VERSION=v1.32
CRIO_VERSION=v1.32" | tee -a ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc
$ curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/$KUBERNETES_VERSION/deb/Release.key |
sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/$KUBERNETES_VERSION/deb/ /" |
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
$ curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/addons:/cri-o:/stable:/$CRIO_VERSION/deb/Release.key |
sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/cri-o-apt-keyring.gpg
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/cri-o-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/addons:/cri-o:/stable:/$CRIO_VERSION/deb/ /" |
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cri-o.list```
そして
cri-oコマンドとKubernetesに必要なkubelet, kubeadm, kubectlの三つのコマンドをインストールして、後者のバージョンを固定する。```bash
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install cri-o kubelet kubeadm kubectl
$ sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl```
スワップをオフにしたりカーネルモジュールをロードしてカーネルパラメータを設定する。
```bash
$ sudo systemctl start crio.service
$ sudo swapoff -a
$ lsmod | grep -e br_netfilter -e overlay
overlay 192512 0
$ echo "overlay
br_netfilter
" | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf
$ sudo modprobe br_netfilter
$ lsmod | grep -e br_netfilter -e overlay
br_netfilter 32768 0
bridge 372736 1 br_netfilter
overlay 192512 0
$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
$ echo "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
" | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
$ sudo sysctl --system
$ sysctl net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables net.ipv4.ip_forward
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1```
ここからはControlPlaneでクラスタを構成して、CNIを入れて他のノードが参加する準備をしていく。
まず、CRI-Oのソケットが存在していることを確認して、
kubeadm initする。```bash
$ ls /var/run/crio/crio.sock -la
srw-rw---- 1 root root 0 Dec 25 02:30 /var/run/crio/crio.sock
$ sudo kubeadm init --cri-socket=/var/run/crio/crio.sock --pod-network-cidr=192.168.0.0/16
W1226 03:06:17.944044 80200 initconfiguration.go:126] Usage of CRI endpoints without URL scheme is deprecated and can cause kubelet errors in the future. Automatically prepending scheme "unix" to the "criSocket" with value "/var/run/crio/crio.sock". Please update your configuration!
[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.32.0
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local sapphire] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.1.110]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost sapphire] and IPs [192.168.1.110 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [localhost sapphire] and IPs [192.168.1.110 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "super-admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[kubelet-check] Waiting for a healthy kubelet at http://127.0.0.1:10248/healthz. This can take up to 4m0s
[kubelet-check] The kubelet is healthy after 500.944574ms
[api-check] Waiting for a healthy API server. This can take up to 4m0s
[api-check] The API server is healthy after 13.50209743s
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node sapphire as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node sapphire as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: irpqxh.pop58b4ha1584q6w
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.1.110:6443 --token irpqxh.pop58b4ha1584q6w \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b406fcfe57a68f99fb82412db52d0206d6218205dc8719425bfc11c19e6f4750```
すると、いくつかコマンドが出力されるので実行して
$HOME/.kube/configを作成しておく。```bash
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
$ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
$ ls -la ~/.kube/config
-rw------- 1 asuto153 asuto153 5657 Dec 26 03:07 /home/asuto153/.kube/config```
これでクラスタが初期化できたはずなので、そうしたらnodeやpodが正常に認識されていそうか確認しておく。
```bash
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
sapphire NotReady control-plane 96s v1.32.0
$ kubectl get pods
No resources found in default namespace.
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-668d6bf9bc-g86dg 0/1 Pending 0 12m
coredns-668d6bf9bc-pwztr 0/1 Pending 0 12m
etcd-sapphire 1/1 Running 0 12m
kube-apiserver-sapphire 1/1 Running 0 12m
kube-controller-manager-sapphire 1/1 Running 0 12m
kube-proxy-g6ktm 1/1 Running 0 12m
kube-scheduler-sapphire 1/1 Running 0 12m```
## Calicoの導入
次に、以下のドキュメントに従ってノード間の通信を行うためのCNI(Container Network Interface)プラグインであるCalicoを導入していく。
まずはCalicoを入れるための
tigera-operatorを導入する。```bash
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.29.1/manifests/tigera-operator.yaml
namespace/tigera-operator created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpfilters.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/caliconodestatuses.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ippools.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipreservations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kubecontrollersconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/tiers.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/adminnetworkpolicies.policy.networking.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/apiservers.operator.tigera.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/imagesets.operator.tigera.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/installations.operator.tigera.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/tigerastatuses.operator.tigera.io created
serviceaccount/tigera-operator created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/tigera-operator created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/tigera-operator created
deployment.apps/tigera-operator created```
マニフェストから
tigera-operatorを生成したら、namespaceとdeploymentとpodにtigera-operatorがいることを確認する。```bash
$ kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 18m
kube-node-lease Active 18m
kube-public Active 18m
kube-system Active 18m
tigera-operator Active 29s
$ kubectl get deployment
No resources found in default namespace.
$ kubectl get deployment -n tigera-operator
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
tigera-operator 1/1 1 1 44s
$ kubectl get pod -n tigera-operator
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
tigera-operator-7d68577dc5-sgmsc 1/1 Running 0 54s```
次に、Calico本体をマニフェストから生成して、
calico-systemというnamespaceにpodが生えてくるのを待つ。```bash
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.29.1/manifests/custom-resources.yaml
installation.operator.tigera.io/default created
apiserver.operator.tigera.io/default created
$ watch kubectl get pods -n calico-system
$ kubectl get pods -n calico-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
calico-kube-controllers-64fc668889-2qcqd 1/1 Running 0 2d12h
calico-node-85rpp 1/1 Running 0 2d11h
calico-node-bxmdx 1/1 Running 0 2d12h
calico-node-qcgbg 1/1 Running 0 2d11h
calico-typha-858dbff796-fqd4c 1/1 Running 0 2d12h
calico-typha-858dbff796-klsl5 1/1 Running 0 2d11h
csi-node-driver-7hb9l 2/2 Running 0 2d11h
csi-node-driver-mhd72 2/2 Running 0 2d12h
csi-node-driver-mpxcq 2/2 Running 0 2d11h
$ kubectl describe node sapphire | grep -i taint
Taints: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule
$ kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane-
node/sapphire untainted
$ kubectl describe node sapphire | grep -i taint
Taints:
$ kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
sapphire Ready control-plane 35m v1.32.0 192.168.1.110 Ubuntu 24.04.1 LTS 6.8.0-1017-raspi cri-o://1.32.0 ```
## クラスタの構成
ここまでできたらあとは他の2つのWorker Nodeから以下のコマンドを実行してクラスタに参加させる。
```bash
$ sudo kubeadm join 192.168.1.110:6443 --token irpqxh.pop58b4ha1584q6w \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b406fcfe57a68f99fb82412db52d0206d6218205dc8719425bfc11c19e6f4750 \
--cri-socket=/var/run/crio/crio.sock```
そしてControl Planeからnodeが認識されていることを確認する。
```bash
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
emerald Ready 2m4s v1.32.0
ruby Ready 3m10s v1.32.0
sapphire Ready control-plane 59m v1.32.0 ```
そうしたら以下のような二つのマニフェストを用意して、applyする。
```yaml:nginx-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80```
```yaml:nginx-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: NodePort```
これでdeployされて、ここで表示されたポートであるhttp://<マシンのIPアドレス>:30379にアクセスすることでnginxのデフォルト画面が表示され、正常に動作していることが確認できた。
```bash
$ kubectl apply -f kubernetes/nginx-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment created
$ kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-deployment 3/3 3 3 24s
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-647677fc66-dhcbt 1/1 Running 0 34s
nginx-deployment-647677fc66-q7vlf 1/1 Running 0 34s
nginx-deployment-647677fc66-wrd4n 1/1 Running 0 34s
$ kubectl apply -f kubernetes/nginx-service.yaml
service/nginx-service created
$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 75m
nginx-service NodePort 10.108.55.243 80:30379/TCP 9s ```
## 今後
今回、おうちkubernetes基盤を構築してnginxを動かすところまではできたが、悲しいことに肝心の動かしたいアプリが今のところ思いついていないので、もし適当なアプリを作るときは次はkubernetesで動かそうと思う。もし誰か面白そうなアイデアを思いついたら教えて欲しい。